Smart industry – what does it mean?

Wisdom can manifest in many ways, but ultimately, smart industrial process solutions are designed, optimized, and built according to the specific needs and characteristics of each sector. Smart industry represents a comprehensive approach that integrates advanced technologies, sustainability practices, and innovation across entire sectors, enabling industries to evolve and thrive in a rapidly changing world. This article will provide more detailed information about the solutions used in both smart industries and smart factories.
What makes a smart factory?
Within the broader context of a smart industry, smart factories are the physical hubs where innovative solutions are implemented. A smart factory is forward-thinking and efficient, characterized by its ability to adapt, optimize, and improve processes in real time. Efficiency is ensured when solutions are neither undersized nor oversized, and when the quick resolution of peak loads is taken into account. In a smart factory, nothing is wasted, and nothing is lacking. Real-time data monitoring and analysis help identify inefficiencies, prevent failures, and optimize resource utilization. Modern automation systems optimize processes, while digital solutions help keep equipment fleets under surveillance. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of equipment.
The importance of smart industry and factory
The vision of a smart industry extends far beyond mere efficiency; it’s about being smart in how we handle the environment, use new technology, and stay strong and adaptable. By integrating advanced technologies like automation, efficient energy and water management systems, and waste-reducing solutions, industries can optimize operations at both the sector and factory levels, minimizing their environmental footprint. Embracing these principles not only ensures operational efficiency but also positions industries as leaders in responsible and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Smart factories are key to making this vision a reality. These factories use advanced technology to control their operations, manage energy and water more efficiently, and reduce waste. By doing this, they help the whole industry meet its goals for being innovative and sustainable. When both industries and factories follow these principles, they show that they are committed to running their operations efficiently and taking care of the environment.
Feasibility studies offer valuable insights and guidance for informed decision-making regarding new or existing plant projects. A plant audit involves a comprehensive assessment of your existing plant’s technical condition. It helps identify potential issues and risks that could impact plant operation, output, and profitability, allowing for timely solutions.
Smart industry examples in factories
1. Efficient energy production and utilization
Efficient energy production and utilization reduces energy loss and improves overall production process efficiency, while also helping to reduce environmental impacts. For example:
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plants can simultaneously produce electricity and heat, increasing the efficiency of the entire system. Such a system significantly reduces energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
Learn more about CHP solutions
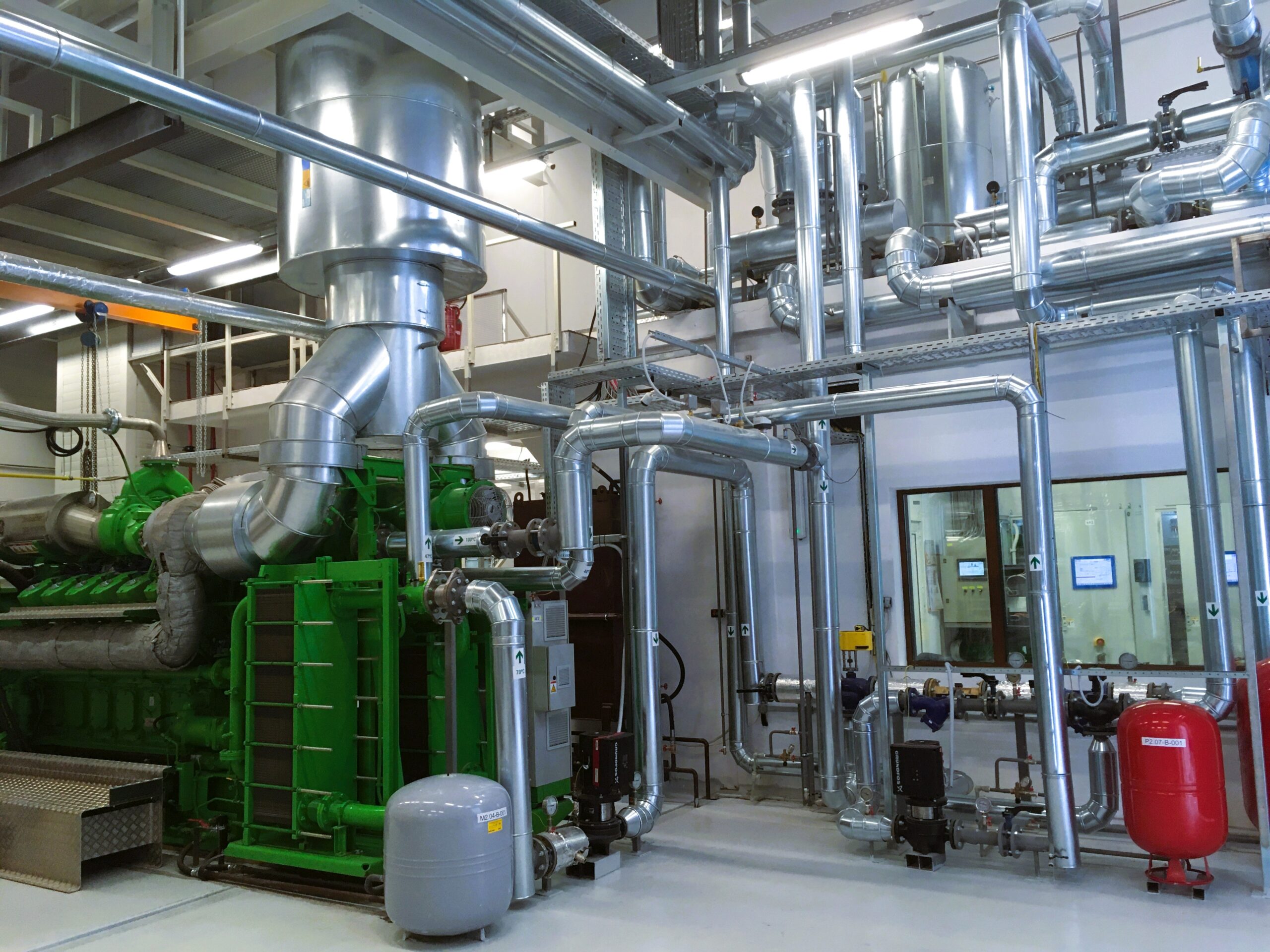

2. Efficient water treatment and management
Efficient water treatment and management help reduce water loss, extend equipment lifespan, and ensure clean, high-quality water for production processes. For example:
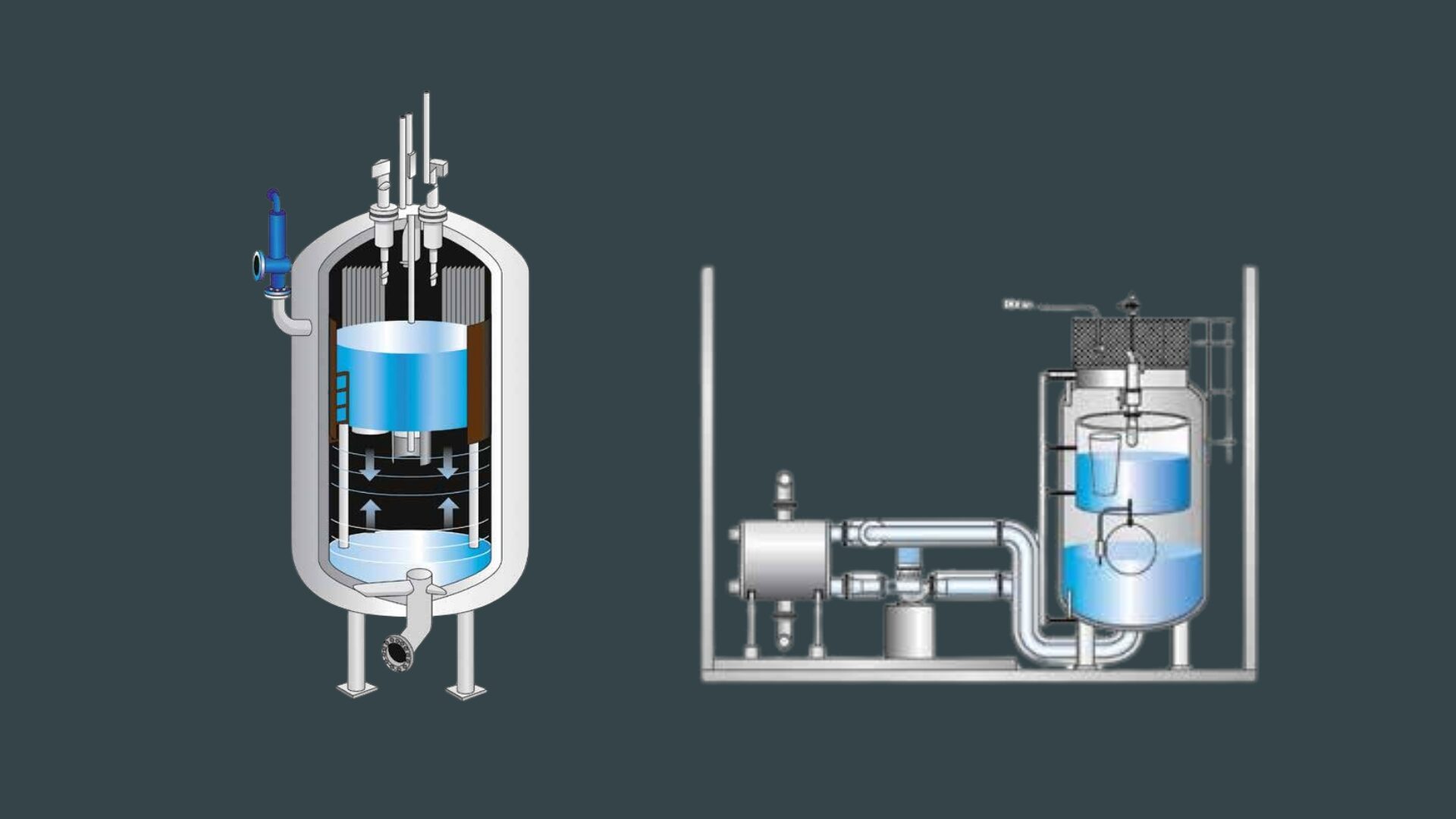
- Water softeners and de-ironers remove compounds that cause water hardness and residual iron, extending the lifespan of the entire boiler plant and ensuring high-quality steam. The filter operates according to water consumption, following economic principles.
- Filtration technologies include pressure filters, activated carbon filters, and bag filters. Pressure filters remove suspended solids by forcing water through filter media under pressure. Activated carbon filters absorb chlorine, VOCs, and impurities, improving taste and odor. Bag filters capture larger particles and debris, offering cost-effective pre-filtration in industrial applications.
- Demineralization plants require no special pre-treatment of the inlet water to achieve demineralized water quality. The plants are used for many applications, including the production of rinse water, process water, boiler water, and more.
- Reverse osmosis (RO) efficiently eliminates pyrogens, microorganisms, and up to 90% of organic substances, ensuring unparalleled water quality. They feature a modular design and are equipped with energy-efficient E-pumps, reducing energy consumption by up to 50% and saving installation time
- Deaerators remove excess oxygen from water, reducing the risk of corrosion and extending the lifespan of the boiler plant. A thermal deaerator is used for reducing the oxygen content of steam boiler feedwater. With a vacuum deaerator, the oxygen content in water can be reduced from 8-10 mg/l to less than 0.2 mg/l.
Learn more about water treatment products
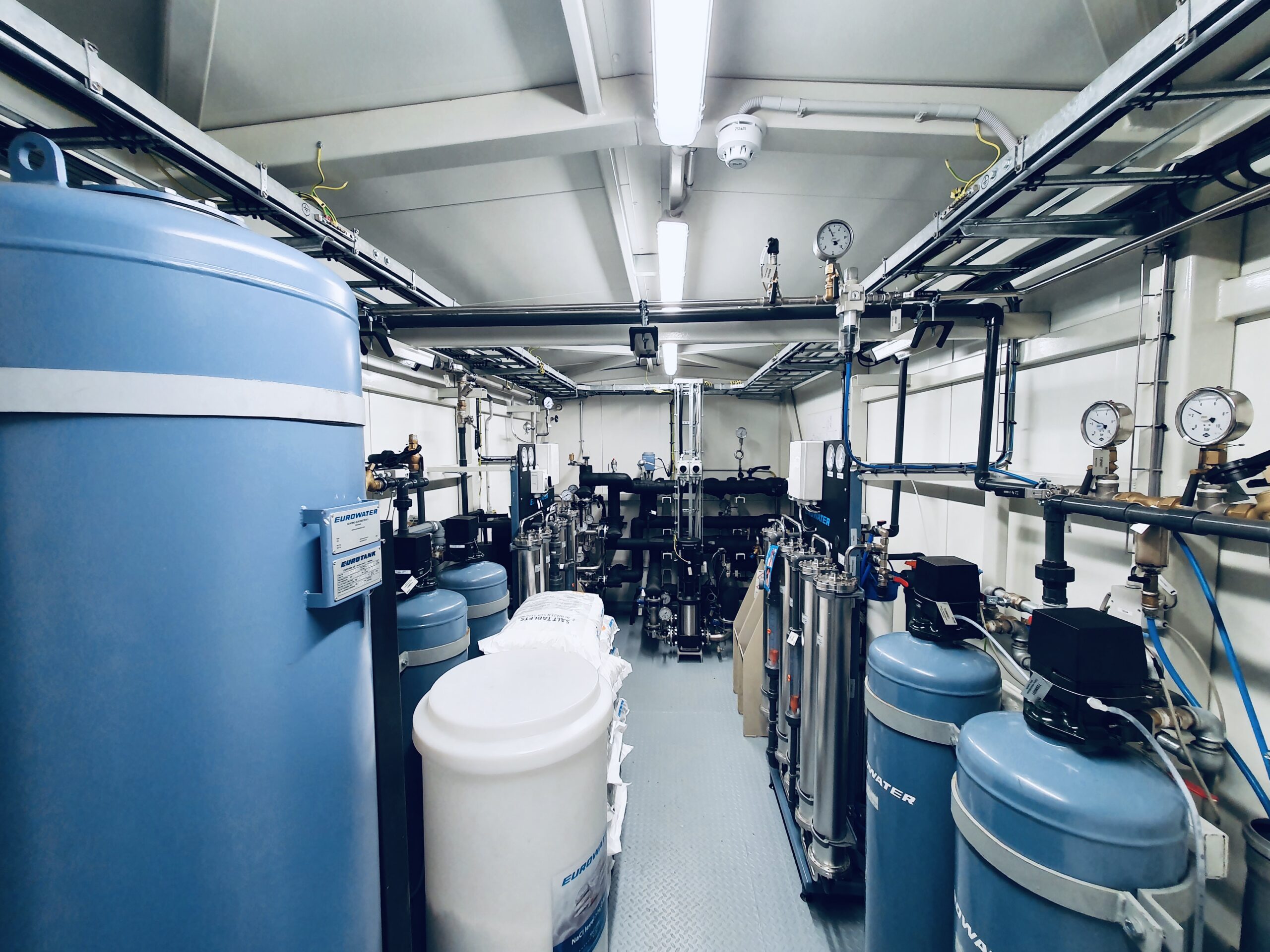

3. Flexible solutions with modular equipment
Flexible solutions with modular equipment involve integrating these technologies effectively into various industrial and operational settings to adapt processes. Modulating capacity heat supply equipment such as biomass boilers, steam boilers, steam generators, boilers and frequency converters are essential components. These technologies enable precise control and adjustment of heat generation and distribution to match varying production demands, ensuring efficient energy use and operational flexibility.
- Biomass boilers offer flexible power modulation ranging from 30% to 100%. This capability allows precise adjustment of heat output in response to varying operational needs. By efficiently utilizing biomass fuel, biomass boilers ensure sustainable energy use while maintaining operational flexibility
- Steam boilers can be used with all common gaseous fuels like natural gas, LPG, LNG, biogas and hydrogen, fuel oils – both heavy and light fuel oils. Their versatility makes them suitable for applications ranging from small-scale heating to large industrial processes.
- Steam generators can meet sharply increased steam demand (peak load handling) and cover fluctuating smaller steam quantities. The generator is more expensive than a conventional steam boiler, but its startup and response time are only a few minutes (compared to several hours for a boiler), with better steam quality and minimal blowdown losses. Due to the absence of a large amount of water to keep warm, there is no energy consumption. This makes the generator an energy-efficient steam solution, which pays off quite quickly depending on the production volume.
- Frequency converters for modulating burners allow the burner fan to operate at low speeds, thereby reducing electricity consumption and noise in the boiler plant. Frequency converter water pumps save electricity and can assess and operate according to actual water demand.
Learn more about industrial boiler house solutions
4. Waste-free solutions
Waste-free solutions focus on maximizing the use of energy and resources while reducing waste and losses. Waste heat is captured, and energy from the process is reused. For example:
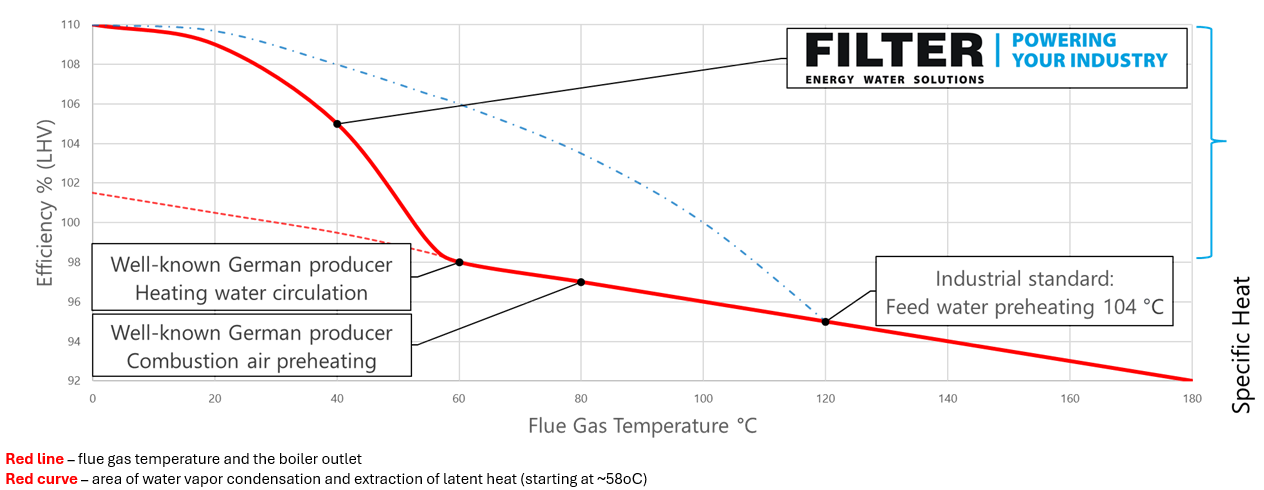
- Waste heat recovery using flue gas heat exchanger can utilize the heat energy from the flue gases. Flue gas heat exchangers extract heat from exhaust gases, which can then be used for various purposes such as preheating combustion air or heating process streams.
- Heat recovery systems capture waste heat flows from cooling water and wastewater and redirect them to further processes.
- A flue gas condensation system for heat recovery utilizes recovered heat from flue gases, which can be effectively used for process heating and industrial applications.
- Capturing the waste heat from production and using it in a heat exchanger to heat water, which can then be raised in temperature by an industrial heat pump. It can then be directed, for example, to satisfy building heating and hot water needs.
- Capturing waste heat from production and utilizing an industrial heat pump to heat water allows for raising its temperature, which can be used to satisfy building heating and hot water requirements.
- Compressor waste heat recovery using heat pump technologies involves capturing excess heat generated during compression processes and using heat pumps to upgrade and transfer this heat for efficient heating purposes.
- Using waste heat from rotating machines to heat the water entering the boiler.
- Reuse of deaerator vent heat through a heat exchanger. Typically, the steam generated is otherwise released into the atmosphere.
- Steam condensate heat exchangers redirect the energy of hot condensate back into the production process, using it to heat other processed fluids (where feasible).
- Condensate recovery systems help collect and return condensed steam to the boiler plant, heating the feedwater going into the boiler and thus reducing water and energy loss.
Learn more about energy recovery systems
5. Environmentally friendly technologies
Optimizing energy use and implementing environmentally friendly solutions help reduce environmental impact and achieve sustainability goals. This may involve using renewable energy, optimizing water and energy use, or using equipment and technologies that reduce or eliminate emissions. For example:
- Connecting a solar thermal park with a biomass boiler is an environmentally friendly solution that also ensures a consistent and continuous supply of heat.
Learn more about solar thermal district heating plants solutions
- Hot water storage tank provides efficiency of heat supply and production balance.
- Electrical steam boilers and electrical hot water boilers efficiently produce steam or hot water using electricity alone, eliminating local emissions. They also enable participation in frequency regulation business, ensuring stable grid operations.
- BESS energy storage allows you to use electricity during times when buying it from the grid is expensive.
Learn more about energy storage systems
- Electrostatic precipitators (ESP) are effective in cleaning up flue gases and significantly reducing air pollution caused by emissions, contributing to achieving CO2 emission reduction targets.
Learn more about flue gas cleaning systems

6. Smart automation
Automation simplifies complex processes and decision-making, allowing for more efficient and smoother production. For example:
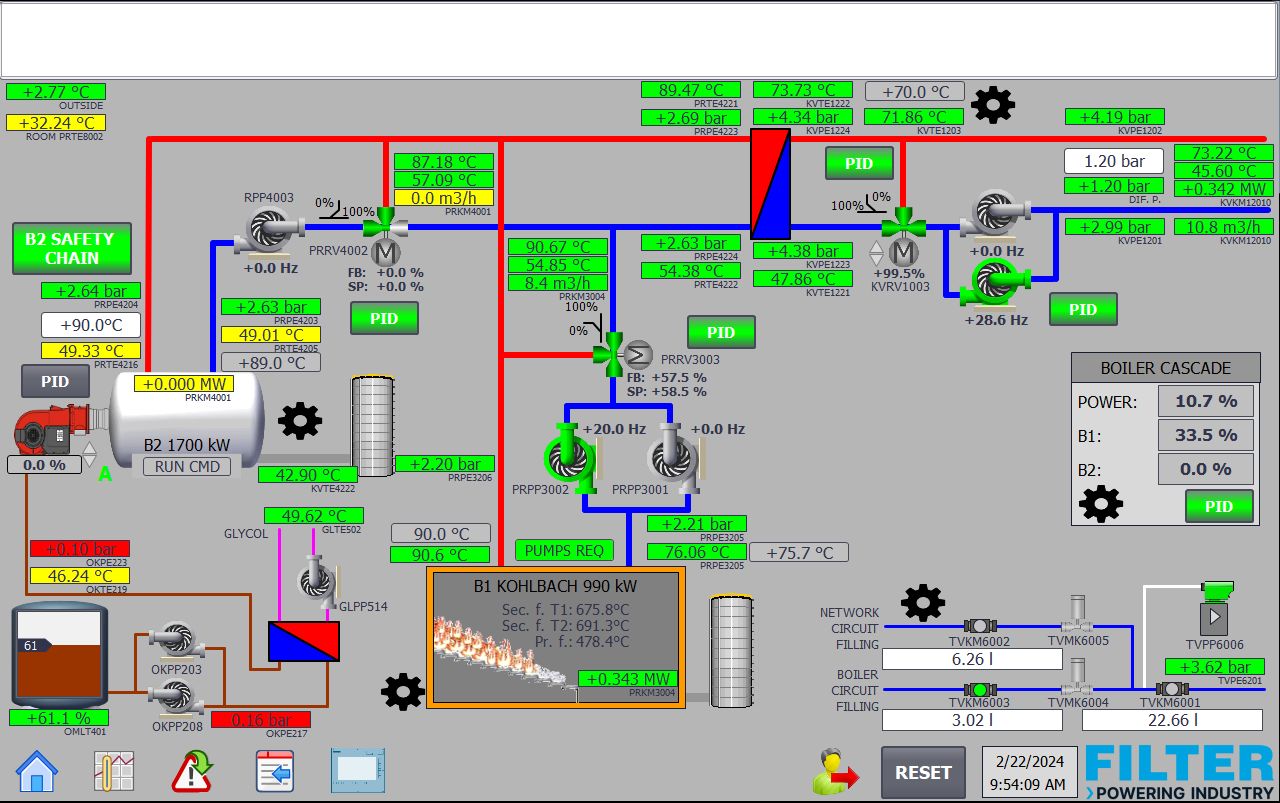
- Field automation utilizing PLCs with advanced algorithms and modern field equipment enables smart and effective control of processing operations.
- SCADA systems offer real-time monitoring and control of processes and store data for smart analytics and decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency and responsiveness.
Learn more about automation solutions
7. Computerized maintenance management system (CMMS)
Paper logs and Excel data sheets are tools of the past. Modern maintenance management software helps manage and plan maintenance tasks conveniently. Proper maintenance plays a significant role in the longevity of equipment, so simplifying maintenance planning and management is advisable. For example:
- Alldevice CMMS maintenance management software, developed in collaboration with the FILTER team, is easy to use for managing both small devices and large machines. Maintenance schedules, reports, manuals, certificates, and other technical information are compactly located in one place.
Learn more about CMMS maintenance management solution

Filter is powering smart industry and smart factories
Filter is dedicated to advancing the transition of industries toward more sustainable and efficient practices. By leveraging innovative technologies and a comprehensive range of solutions, Filter supports industries and factories in achieving their goals for smart consumption and sustainability. The approach begins with a detailed assessment of each client’s needs, leading to customized solutions designed to deliver maximum efficiency and cost savings. Services provided encompass the full spectrum, from feasibility studies and design to construction and maintenance.
With an extensive array of energy and water solutions, Filter is well-positioned to assist industrial clients in their journey toward greener energy solutions and sustainability. For more information on improving industrial efficiency with green energy and water solutions, get in contact with us, a free consultation is available.