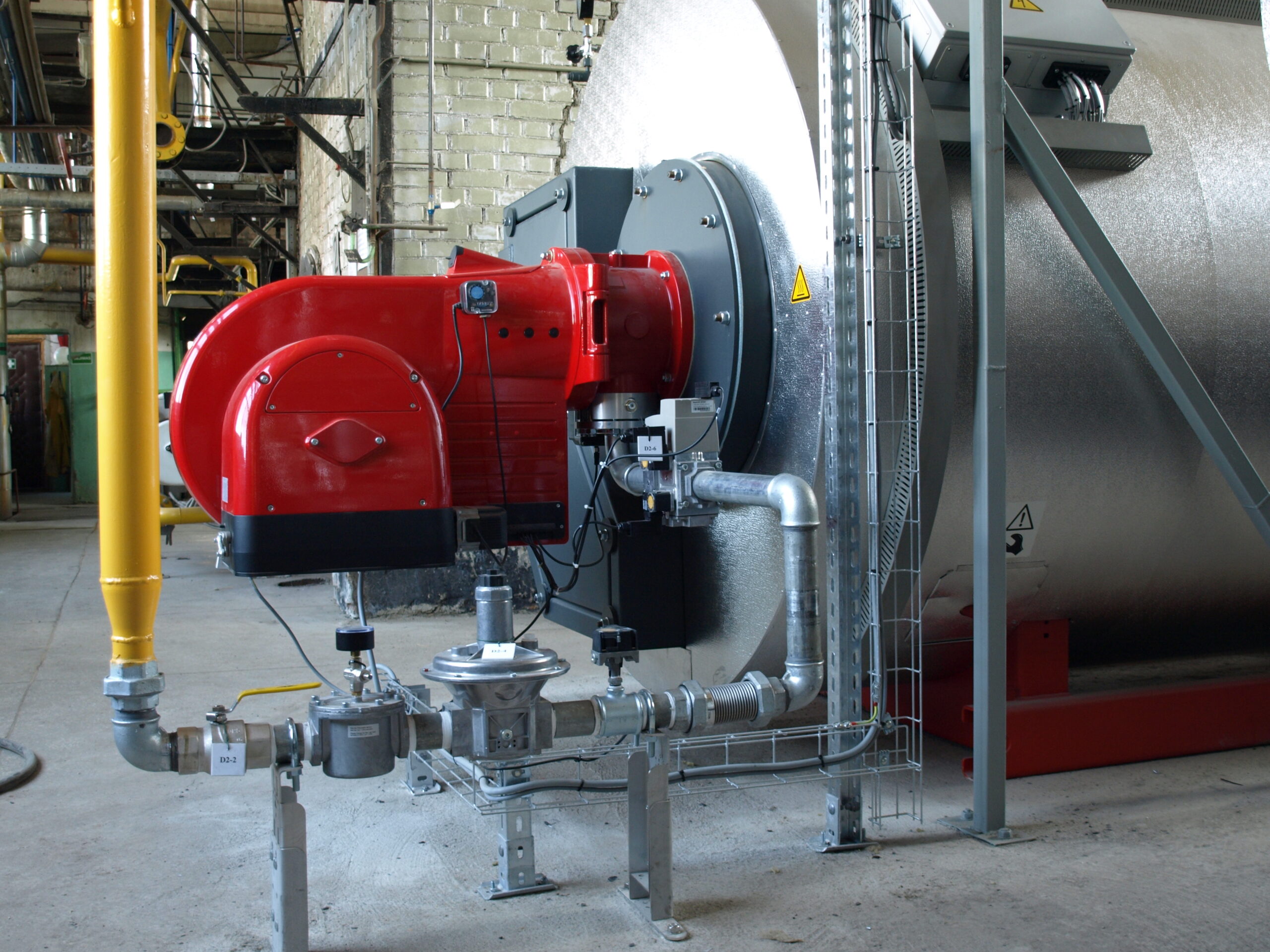
Selecting the appropriate industrial burner is crucial for maximizing efficiency and guaranteeing optimal performance in various applications. With numerous types of burners available, each designed for specific uses and fuel types, understanding their differences and benefits is important for making an informed decision.
Choosing the right burner can significantly impact your operational costs and environmental footprint. It’s not just about the type of fuel the burner uses, considerations include the burner’s efficiency, emission levels, maintenance requirements, and suitability for specific industrial processes. Investing in the right technology can lead to substantial savings and a reduced carbon footprint, which is increasingly important in today’s regulatory environment. Additionally, the right burner can better operational safety, reduce downtime, and improve overall production quality by providing consistent and reliable heat.
Burner applications in industrial settings
Industrial burners are essential components in a wide range of industries, providing the necessary heat for processes such as power generation, manufacturing, and chemical production. Understanding the specific applications and requirements of different types of burners can help industries choose the most suitable solutions for their needs.
Burners are used in various sectors, including food processing, metal production, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals. In the food industry, precise temperature control provided by burners is crucial for processes such as baking, drying, and sterilization. In metal production, high-temperature burners are required for melting and heat treatment processes. In the petrochemical industry, burners are essential for processes such as refining and chemical synthesis. These applications require burners that can operate at high temperatures and maintain a stable flame to ensure consistent product quality. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, burners are used for various heating processes, including sterilization and drying, where precise burner temperature control is critical for ensuring product safety and efficacy. Each application demands specific burner features, such as flame stability, adjustable heat output, and compatibility with different fuel types, underscoring the importance of selecting the right burner for each industrial setting.
Different types of industrial burners
Industrial burners come in many types, each designed to handle different fuels and applications. The most common types include gas burners, oil burners, dual-fuel burners, and hydrogen burners. Each type has its unique advantages and is suited for specific industrial processes.
Gas burners
Gas burners are widely used in industrial applications due to their efficiency and clean-burning properties. They are designed to burn natural gas or other gaseous fuels, providing a consistent and controllable heat source. Gas burners are commonly used in power plants, steam boilers, and various manufacturing processes. They are integral to burner management systems, guaranteeing optimal combustion and efficiency. Gas burners also come in various designs to suit different applications. For example, premix gas burners mix the fuel and air before combustion, creating a stable flame that is efficient and reduces emissions. Forced draft burners use fans to supply air, improving control over the combustion process and allowing for higher burner efficiency and lower emissions. These advancements make gas burners a versatile choice for many industrial applications.
Oil burners
Oil burners are designed to burn liquid fuels such as diesel or heavy oil. These burners are often used in industries where the gas supply is unreliable or unavailable. Oil burners are known for their high heat output and are typically used in burners, furnaces, boilers, and other high-temperature applications. Advanced oil burners now feature improved burner efficiency and reduced emission rates, making them a viable option for many industrial processes.
Oil burners are particularly useful in remote locations or facilities without access to natural gas infrastructure. They can be equipped with various technologies to improve their performance, such as atomizing nozzles that create a fine mist of fuel for more efficient combustion, and preheaters that warm the oil to improve its flow and combustion characteristics. These innovations help oil burners achieve high efficiency and low emissions, making them a practical choice for many industrial settings.

Dual fuel burners
Dual fuel burners offer the flexibility to switch between gas and oil, depending on availability and cost. This versatility makes them an attractive option for industries looking to optimize fuel use and reduce operational costs. Dual fuel burners are commonly used in power plants, industrial boiler burners, and process heating applications. Their ability to operate on multiple fuels makes them a key component in burner management systems, allowing for smooth transitions between fuel sources.
The capability to switch fuels provides operational flexibility and resilience against fuel supply disruptions or price fluctuations. Dual fuel burners are equipped with control systems that helps comfortably switch fuels based on predefined criteria, guaranteeing continuous operation and optimal efficiency. This adaptability makes dual-fuel burners a valuable asset in industries where fuel availability and costs can vary significantly.

Hydrogen burners
Hydrogen burners are an emerging technology that offers a clean and efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuels. These burners are designed to burn hydrogen, producing water as the only byproduct. Hydrogen burners are gaining popularity in industries looking to reduce carbon emissions and comply with stringent environmental regulations. As hydrogen production and storage technologies advance, hydrogen burners will likely become more prevalent in industrial applications.The use of hydrogen as a fuel offers significant environmental benefits, as it eliminates CO2 emissions and reduces other pollutants. Hydrogen burners are being developed to meet the specific needs of various industrial processes, including high-temperature applications and processes requiring precise control over flame characteristics. As the hydrogen economy grows, hydrogen burners are expected to play a crucial role in achieving sustainable industrial operations.
Natural gas burners: an overview and their benefits
Natural gas burners are among the most efficient and environmentally friendly options available for industrial applications. They offer several benefits – including high efficiency, low emissions, and cost-effectiveness. Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel that produces fewer pollutants compared to oil or coal, making it an ideal choice for industries looking to reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, natural gas heating values often feature advanced burner management systems to create optimal performance and safety.
Natural gas burners are also known for their operational flexibility and ease of maintenance. They can be easily integrated into existing industrial systems, providing a reliable and consistent source of heat. The lower maintenance requirements of natural gas burners translate into reduced downtime and lower operating costs, making them a cost-effective solution for many industries.
The role of natural gas in power plants, generators and engines
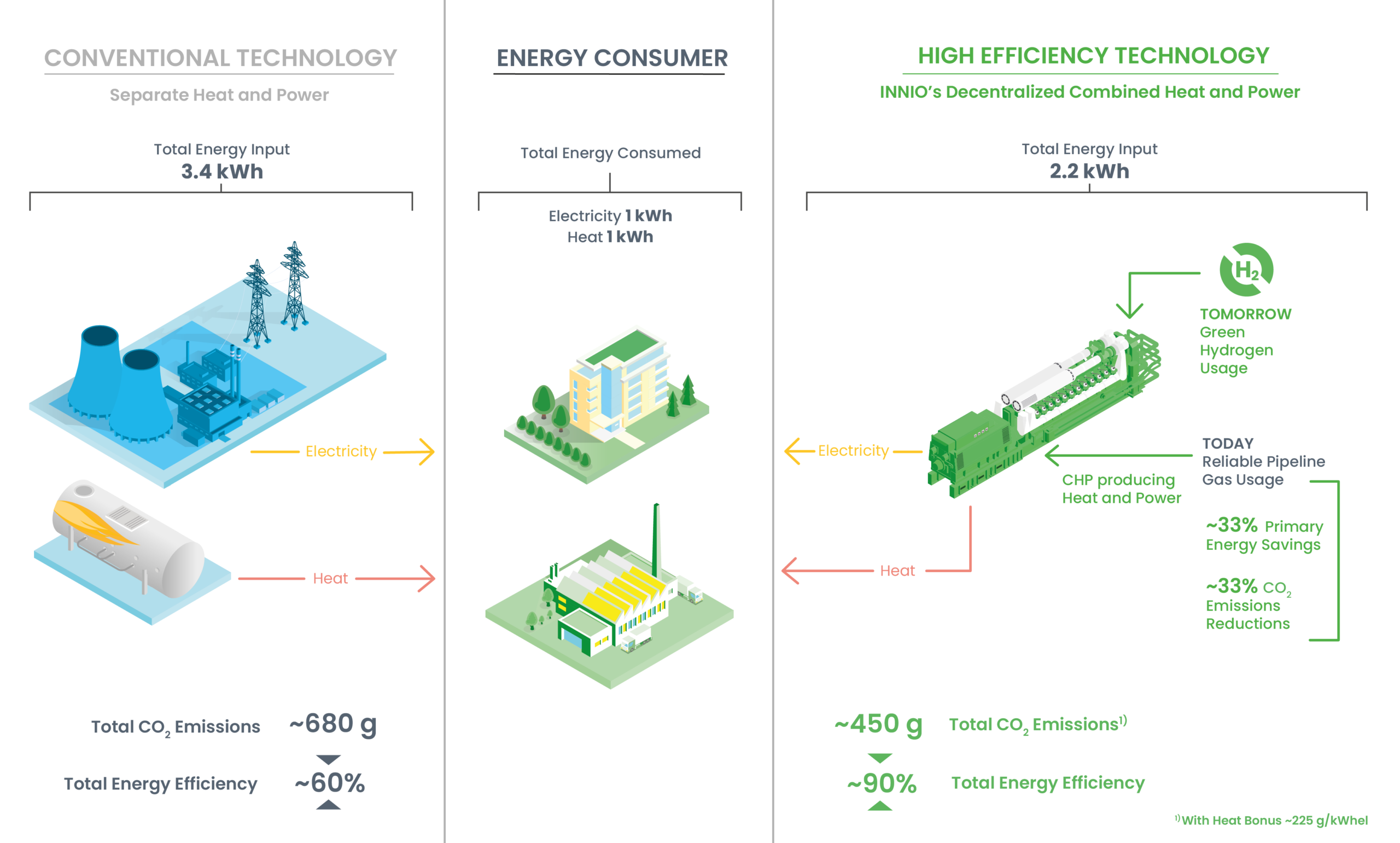
Natural gas plays a vital role in powering various industrial applications, including power plants, generators, and engines. Its high calorific value calculation of natural gas and clean-burning properties make it an excellent fuel for natural gas electricity generators and powering industrial processes. Natural gas engines are widely used in natural gas combined heat and power (CHP) systems, which improve overall efficiency by capturing and utilizing the heat produced during electricity generation.
In power plants, natural gas cogeneration is often used in combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) systems, where gas turbines generate electricity and the waste heat is used to produce steam for additional natural gas power generators. This process significantly improves the overall efficiency of power generation and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Natural gas formulas are also used for peak shaving, providing additional power during periods of high demand, and guaranteeing a stable and reliable electricity supply.
Natural gas generators: efficiency and applications in industrial settings
Natural gas generators are widely used in industrial settings for their efficiency and reliability. These generators convert natural gas into electricity, providing a consistent and cost-effective power source. Small natural gas generators are commonly used in backup power systems, remote locations, and industries where uninterrupted power supply is critical. Industrial generators running on natural gas can range from small units to large power plants, catering to diverse energy needs.
For larger industrial requirements, there are options like 700 kW natural gas generators, 70 kW natural gas generators, 60 kW natural gas generators, and others. For smaller needs, 10 kW generators natural gas and 8 kW natural gas generators are ideal. Medium to large setups can benefit from 450 kW natural gas generators, 40 kW natural gas generators, and 30 kW natural gas generators. The versatility of 250 kW natural gas generators and 250 kVA natural gas generators makes them adaptable to various applications.The choice of industrial burners and natural gas generators is crucial for achieving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact. By understanding the specific needs and applications of each burner type, industries can make informed decisions that improve their productivity and sustainability. Filter offers a comprehensive range of burners and generators designed to meet the diverse requirements of modern industrial operations.
Other burners types
In addition to the common types mentioned above, there are several specialized burners designed for specific applications. These include melting burners, thermal burners, ray burners, oxy burners, and oxygen burners. Each of these burners offers unique benefits for specific industrial processes. For example, oxy burners and oxy-fuel burners are used in high-temperature applications and provide increased efficiency by using pure oxygen instead of air for combustion.
Melting burners are specifically designed for metal melting applications, providing high heat output and precise control to ensure uniform melting. Thermal burners are used in processes that require consistent, high-temperature heat, such as thermal oxidizers and kilns. Rayburners and radiant tube burners provide radiant heat for processes requiring direct, intense heat. These specialized burners are critical for optimizing specific industrial processes, guaranteeing efficiency, and achieving desired outcomes.
Choosing the right burner: from oil burners to hydrogen burners
Selecting the right burner involves considering various factors such as fuel availability, efficiency, environmental impact, and cost. Industries need to assess their specific requirements and choose a burner that meets their operational needs while minimizing emissions and fuel costs. For instance, process burners used in chemical manufacturing will have different specifications compared to a burner used in a steam boiler. Understanding the specific demands of each application is key to making the right choice.
The choice of burner fuel also depends on regulatory requirements and environmental considerations. Industries must comply with emission standards and regulations, which can influence the selection of burners. Advanced burner technologies, such as ultra-low NOx burners and hydrogen burners, can help industries meet these standards while maintaining high efficiency. Additionally, the availability of technical support and maintenance services is crucial for guaranteeing the long-term performance and reliability of the selected burner.
Selecting the right burner is not only about immediate operational needs but also about future-proofing your industrial processes. Investing in burners that can adapt to changing fuel availability or regulatory standards creates long-term sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Consulting with experts and conducting a thorough analysis of your industrial requirements will be helpful in making the most informed decision.
Filter is powering burners industry ranging from 15 kW to 90 MW
Filter offers a comprehensive range of burners, catering to diverse industrial needs from 15 kW to 90 MW. Our advanced burner technology ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations. Whether you require a small gas burner for a steam boiler or a large-scale burner for a power plant, we have the expertise and products to meet your needs.Filter’s burners are designed to deliver reliable and consistent performance across various industrial applications. Each burner is engineered to provide maximum efficiency, helping you reduce operational costs and minimize your environmental footprint. Filter’s commitment to customer satisfaction means you can rely on our products to meet the highest standards of safety and performance. We also offer comprehensive support and maintenance services to ensure your burners operate at peak efficiency. Our team of experts is ready to assist you with installation, troubleshooting, and ongoing maintenance, making sure that your industrial processes run smoothly and efficiently. Don’t compromise on quality and efficiency for your industrial heating needs. Choose Filter for your burner solutions that power your operations effectively and sustainably!



