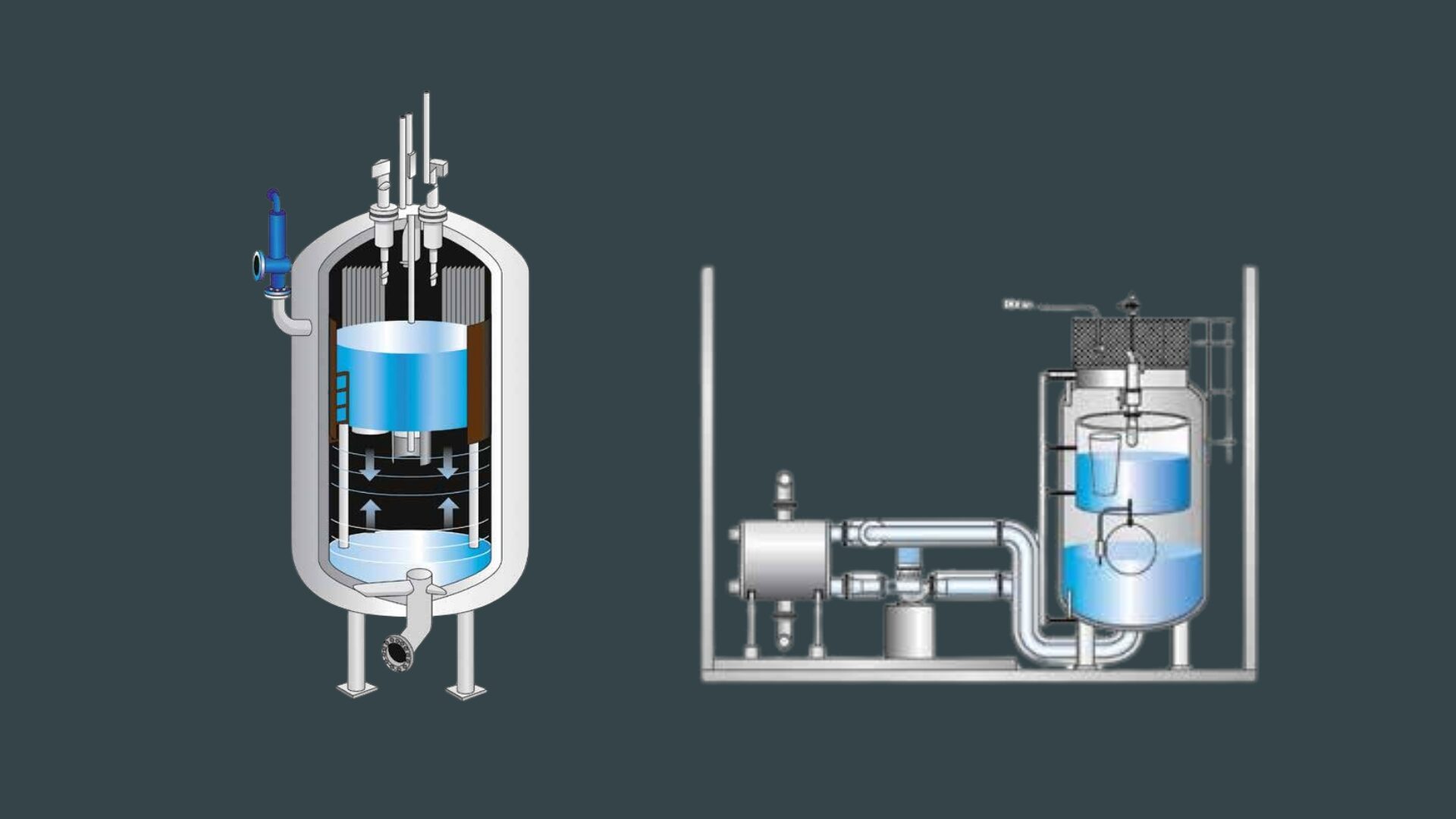
Advanced technology for sustainable heat production
In today’s energy-conscious world, the demand for sustainable, clean, and efficient heating solutions is growing rapidly. Electrode boilers, used for both hot water and steam generation, are among the most advanced and eco-friendly heating technologies available.
At FILTER, we specialize in delivering and commissioning high-performance electrode boiler systems that help reduce carbon footprints, stabilize energy grids, andprovide reliable, cost-effective heating for industrial and municipal applications
1. What are electrode boilers?
An electrode boiler is a fully electric heating system that generates heat by passing electrical current through water. The heat is produced by the natural resistance of water when current flows between submerged electrodes, eliminating the need for fuel or combustion.
Because there is no burner or chimney system, electrode boilers provide zero-emission heating and can be used in a wide range of applications, including:
- District heating
- Industrial process heating
- Steam production for manufacturing and power plants
- Grid balancing and frequency regulation
Types of electrode boilers
- Hot water electrode boilers – designed for district heating and process heating, these systems produce hot water on demand through the resistance of water between submerged electrodes. The result is a clean, efficient, and flexible solution for heating networks and industrial facilities.
- Steam electrode boilers – developed for industrial and large-scale energy applications. With fast response times and precise control, steam electrode boilers provide reliable and emission-free steam for manufacturing, chemical, and energy production industries.
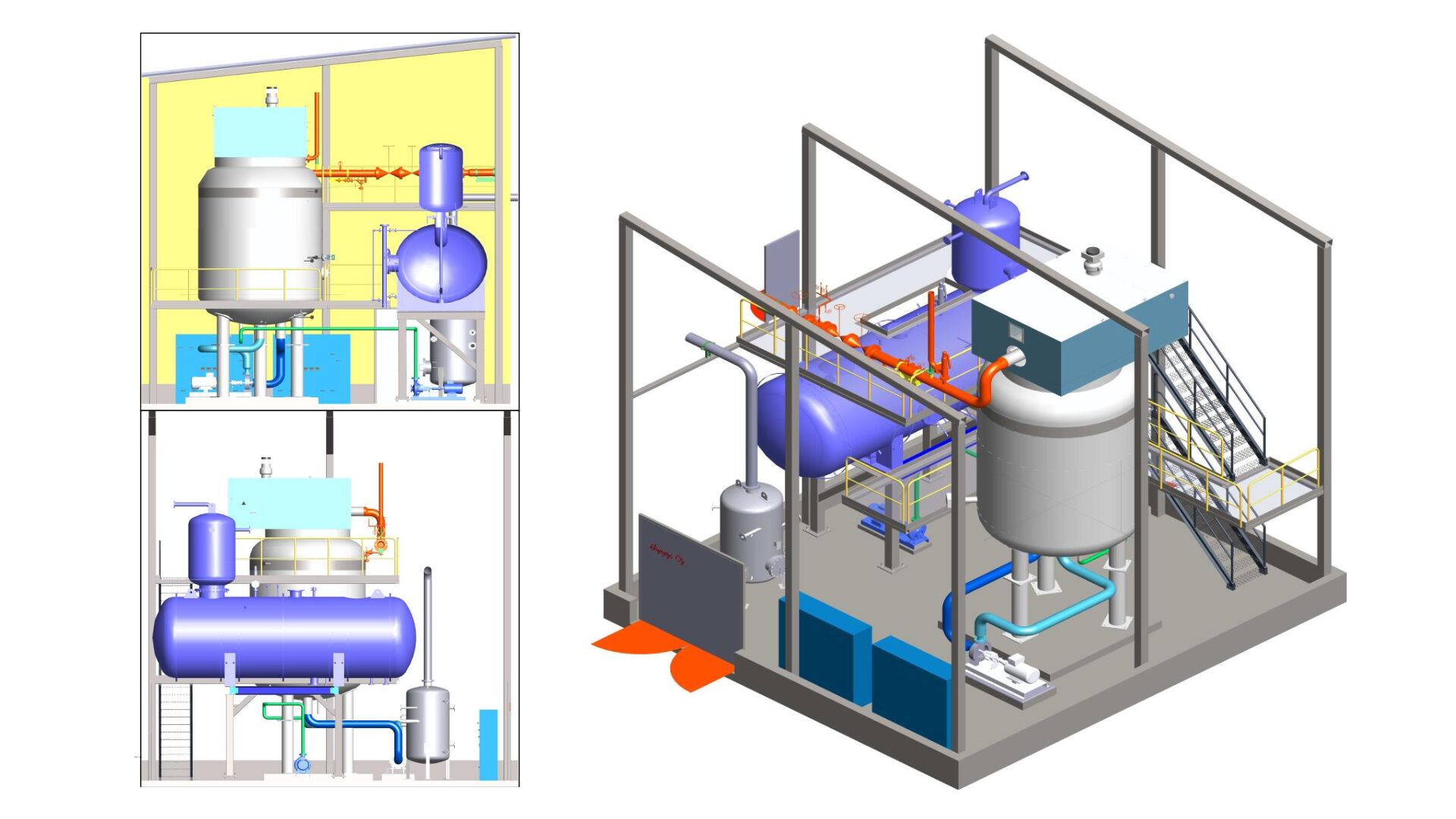
More about steam electrode boilers
2. Electric vs. Electrode boilers
The key difference between electric boilers and electrode boilers lies in their heating method, power capacity, and grid connection.
Electric boilers – use heating elements (immersion coils) to heat water directly in the boiler tank. Ideal for smaller-scale applications connected to the low-voltage distribution network (380–690 V).
Power range: 250 kW – 5,500 kW | Efficiency: up to 99.6% | Pressure: up to 16 bar | Temperature: up to 190°C | Energy source: electricity (380/400/690 V).

Electrode boilers – Use submerged electrodes to pass current through water, generating heat via electrical resistance. Connected to the high-voltage grid (6–24 kV), ideal for large-scale or industrial applications requiring high thermal output and flexibility.

Power range: 5 MW – 60 MW | Voltage: 6–24 kV | Efficiency: above 97% | Fully automated operation | Usable for grid frequency regulation.
Electric boilers are perfect for low-voltage, small-scale systems, while electrode boilers are engineered for high-voltage, high-capacity applications, offering rapid response, zero emissions, and grid flexibility.
3. Hot Water Electrode Boiler – Typical P&ID Overview
The hot water electrode boiler is a high-efficiency, emission-free system that converts electrical energy directly into thermal energy using submerged electrodes. The Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) below illustrates the system layout and operating principle — showing how heat is generated and distributed safely and efficiently without combustion.
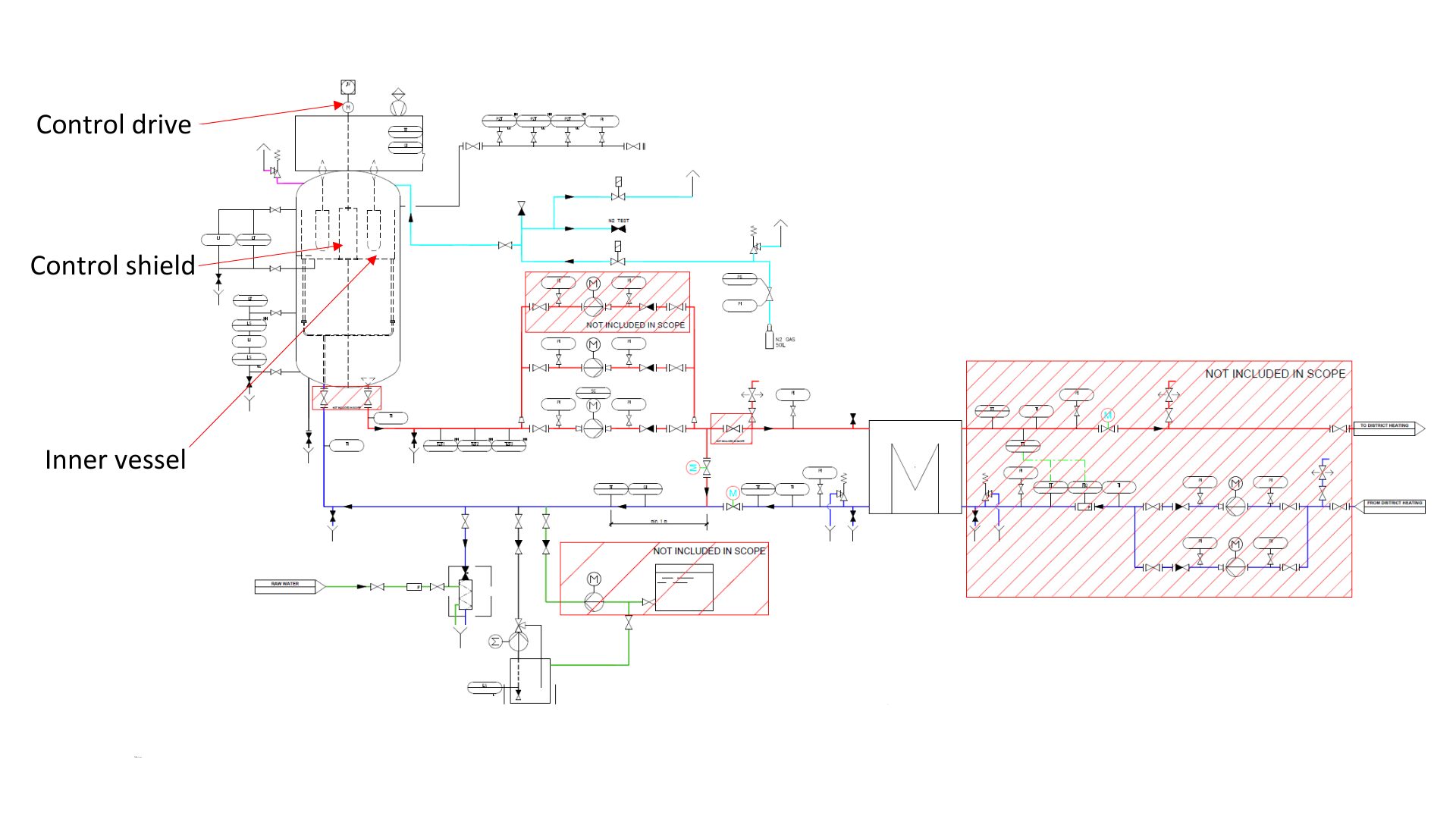
How it works
- Electrical current flows between electrodes submerged in the boiler water.
- The natural electrical resistance of the water converts electrical energy into heat.
- Circulation pumps ensure continuous water flow and uniform heat distribution within the heating circuit.
- The feedwater system maintains optimal water level and conductivity, both critical for stable boiler operation.
- Safety and automation systems continuously monitor and control pressure, temperature, and operating conditions.
More about hot water electrode boilers
Power regulation
The power output of the electrode boiler is regulated by changing the immersion depth of the electrodes in the water.
By adjusting the water level inside the inner vessel, the system controls how much of each electrode is in contact with the water — and therefore how much current flows through it.
When the electrodes are immersed deeper, the contact area increases, allowing more electrical current to pass through the water and raising the boiler’s power output. Conversely, reducing the immersion depth decreases the contact area and lowers the boiler’s power output.
This direct and continuous power regulation allows the electrode boiler to respond rapidly to load changes, achieving full modulation from 0–100% output in less than 60 seconds. This capability makes it particularly well-suited for district heating, industrial processes, and grid-balancing applications that require flexible and dynamic operation.
4. Steam electrode boilers – high-voltage solutions for large-scale applications
Steam electrode boilers work on the same principle as hot water models but are designed for higher power and pressure requirements. Key performance data:
- Power range: 5 MW – 60 MW
- Voltage: 6–24 kV
- Maximum pressure: up to 85 bar(g)
- Efficiency: near 100%
Applications:
- Combined heat and power (CHP) plants
- Industrial steam production
- District heating networks
- Grid frequency and load balancing
With precise temperature control and instantaneous response, steam electrode boilers offer high efficiency, reliability, and flexibility — making them an ideal choice for renewable, large-scale heating and industrial energy systems.
5. FILTER’s electrode boiler projects in the Baltics and Nordic Region
FILTER designed, installed, and commissioned a 9 MW electrode boiler for Estonia’s largest renewable energy producer. The system provides efficient, 100% emission-free heat for the district heating network, stabilizes CHP operations, and supports energy grid balancing.
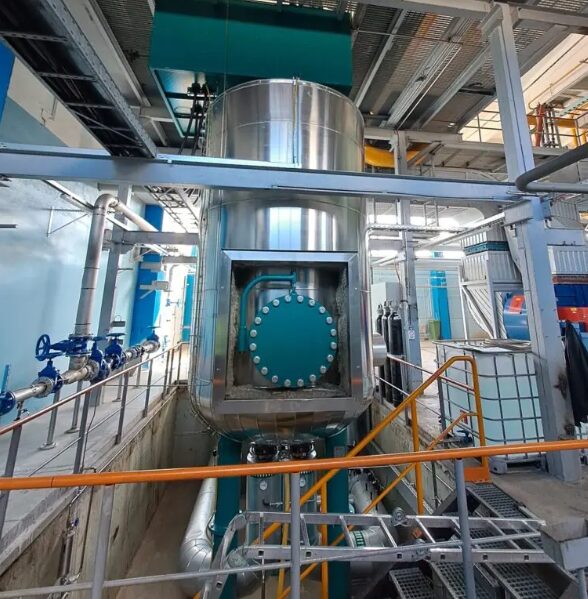

9 MW electrode boiler – Estonia
FILTER is delivering four 50 MW electrode boilers for Helen Ltd, one of Finland’s leading energy companies. Installed in Helsinki’s Hanasaari energy block, this 200 MW electric boiler plant forms part of Europe’s largest heat production complex, operating together with 1,000 MWh of thermal energy storage. The project enables flexible switching between electricity and heat production, setting a new benchmark for urban sustainability.

4×50 MW electrode boilers – Helen Ltd, Finland
FILTER delivered Latvia’s first-ever 50 MW electrode boiler to the Rīgas Siltums heat plant in Imanta.
This system utilizes low-cost electricity to produce renewable heat during off-peak hours, reducing CO₂ emissions and lowering heating costs for the local community.
FILTER’s engineering team continues to oversee installation and commissioning to ensure optimal long-term performance.
6. Why choose FILTER’s electrode boilers
FILTER’s electrode boiler solutions deliver measurable benefits for operators, energy companies, and municipalities:
- Emission-free operation – 100% electric, no fuel or combustion gases
- High efficiency – Near-total energy conversion
- Rapid load control – Full power modulation in under 60 seconds
- Fully automated – Minimal operator involvement
- Scalable power output – From 5 MW to 60 MW
- Flexible use – District heating, industrial steam, and grid balancing
7. Partner with FILTER for sustainable heating
With extensive experience in large-scale electrode boiler systems across Northern Europe, FILTER provides complete solutions for clients seeking to decarbonize heat production and improve energy efficiency.
Whether your goal is to support renewable electricity integration, stabilize your district heating network, or transition away from fossil fuels — FILTER’s electrode boiler solutions are engineered to deliver reliable, efficient, and sustainable heat for decades to come.
Contact us to learn how we can support your next project and accelerate your path toward a carbon-neutral future.