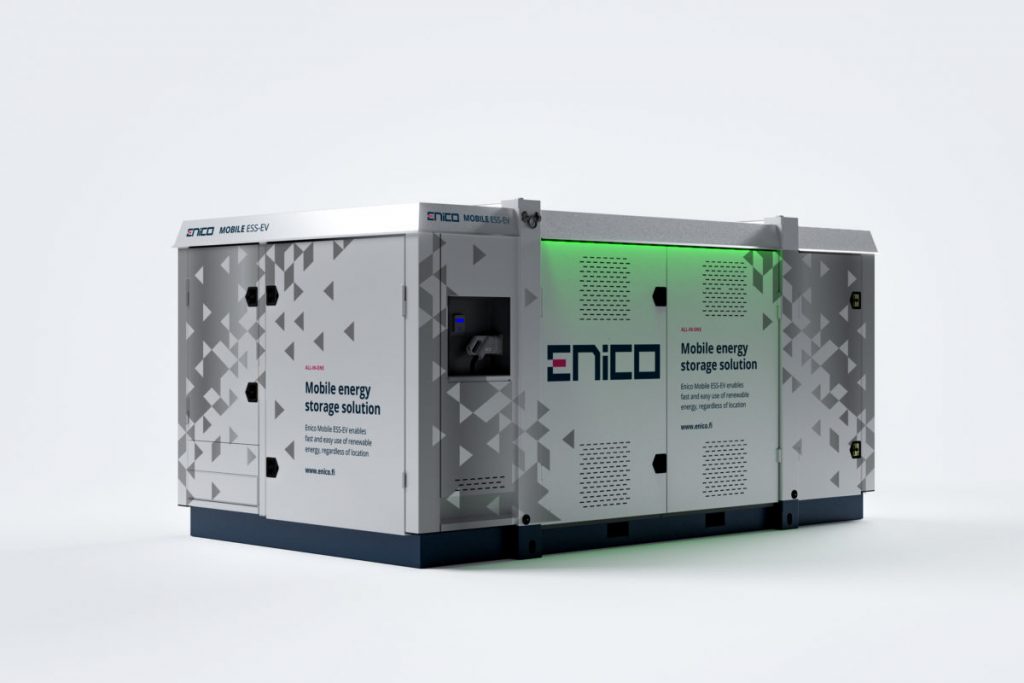
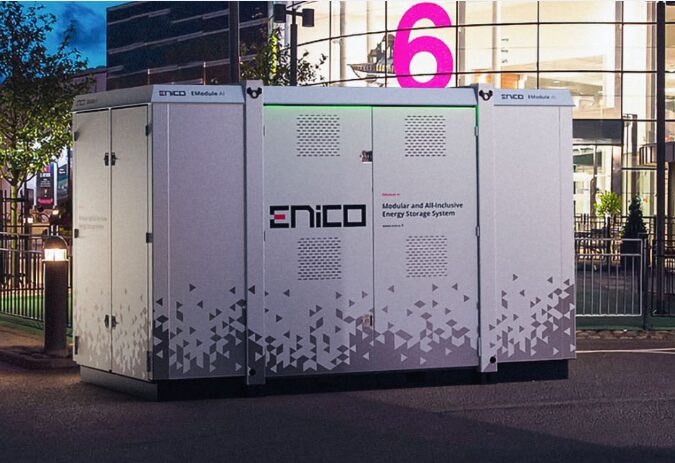
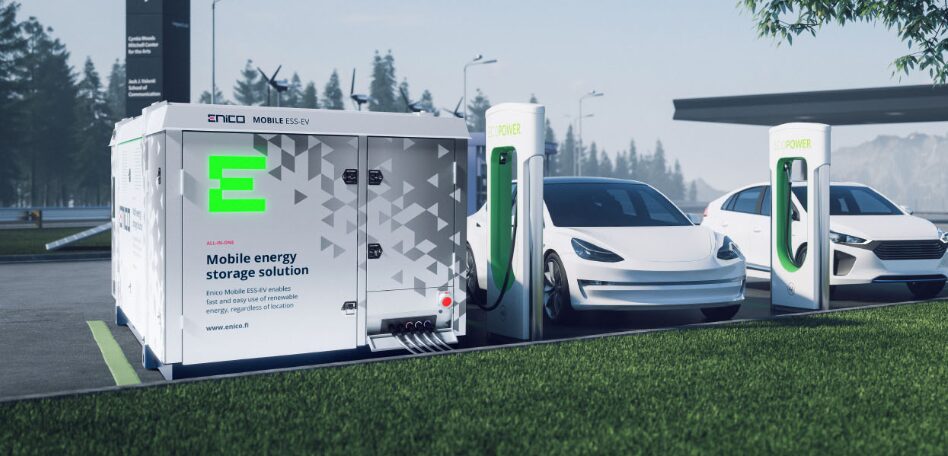
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is a technology that stores electrical energy in batteries for later use. It typically consists of one or more batteries, a battery management system (BMS) for monitoring and controlling the batteries, and power conversion systems (inverters) to convert the stored DC energy into AC electricity when needed. BESSs are used to store energy generated from renewable sources like solar or wind power, to provide backup power during outages, to manage peak electricity demand, and to improve the stability and reliability of electrical grids. They play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy into the grid and enhancing energy efficiency.
-
Reliability
-
Efficiency
-
Sustainability
-
Cost savings
-
Stability